
Emai:marketing@yakkaa.com
業務谘詢專線:400-780-8018
Tel: +1(626)986-9880(U.S. - West Coast)
0044 7790 816 954 (Europe)
Email: marketing@medicilon.com
地址:上海市浦東新區川大路585號
郵編:201299
電話:+86 (21) 5859-1500(總機)
傳真:+86 (21) 5859-6369






© 2023 上海hjc黄金城生物醫藥股份有限公司 保留所有權利 滬ICP備10216606號-3
滬公網安備 31011502018888號 | 網站地圖

業務谘詢
中國:
Email: marketing@yakkaa.com
業務谘詢專線:400-780-8018
(僅限服務谘詢,其他事宜請撥打川沙總部電話)
川沙總部電話: +86 (21) 5859-1500
海外:
+1(626)986-9880(U.S. - West Coast)
0044 7790 816 954 (Europe)
Email:marketing@medicilon.com





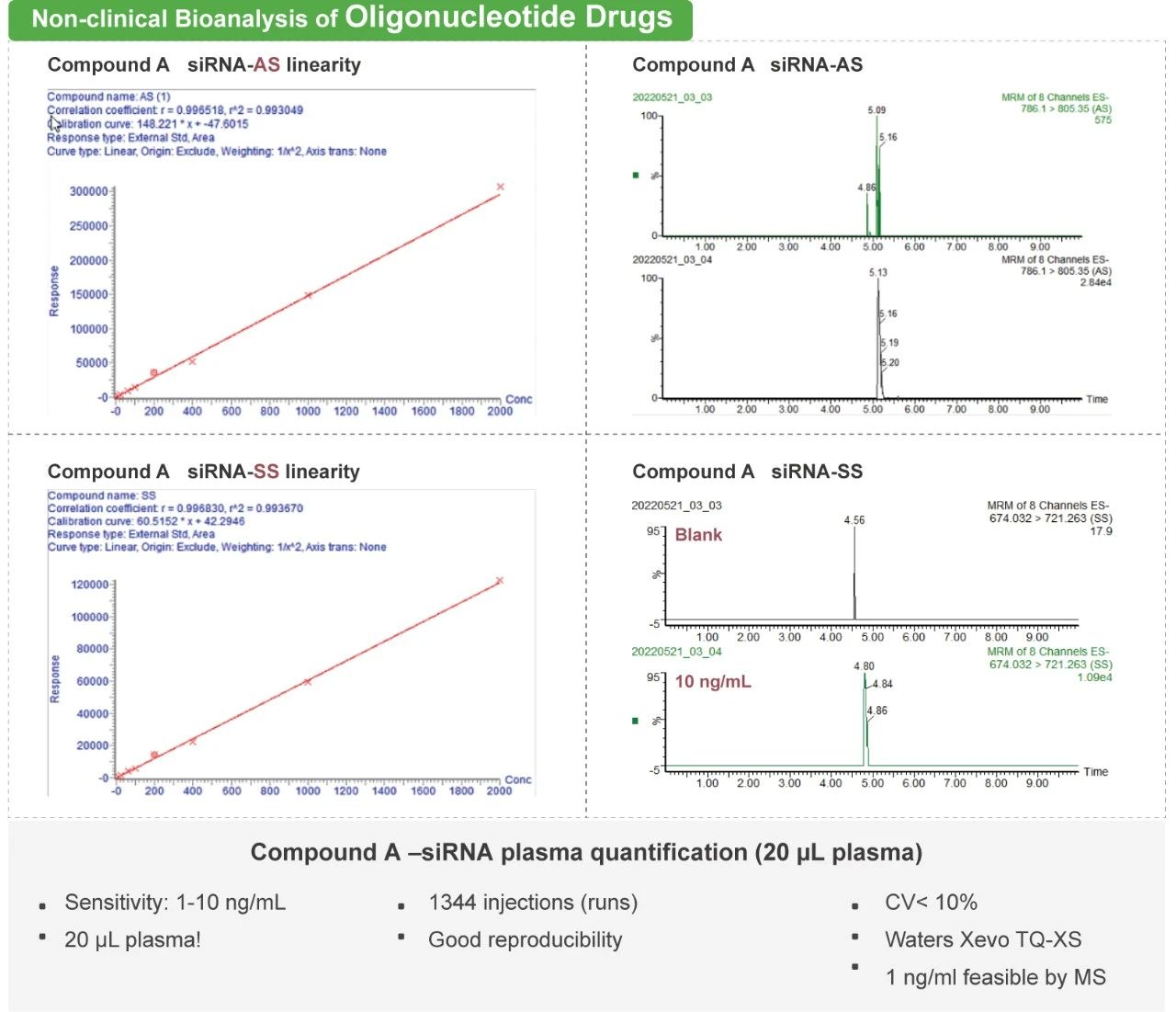
DMPK (Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics) considers how the drug is metabolized and processed by the body. DMPK services help support drug developers in understanding the Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) processes of compounds or drugs. Pharmacokinetics (PK) is the study of the time course of the ADME of a drug, compound or new chemical entity (NCE) after its administration to the body. ADME test results can be used to predict how the drug will behave in the body and to assess its potential for drug-drug interactions (DDIs) with other drugs. Bioanalytical support plays a vital role during the lead optimization stages. Bioanalytical tools can play a significant role and impact the progress in drug discovery and development. Dramatic increases in investments in new modalities beyond traditional small and large molecule drugs, such as peptides, oligonucleotides, cell and gene therapy, mRNA, PROTAC and XDC, necessitated further innovations in bioanalytical and experimental tools for the characterization of their ADME and PK properties.
Gain access to an integrated network of facilities, including DMPK R&D centers across China and the United States. Medicilon’s DMPK&BA department offers a full range of discovery screening, IND-enabling and clinical drug metabolism, pharmacokinetic platforms and services in the following areas: in vitro ADMET, in vivo PK, MetID, Radiolabeled DMPK/ADME, BA, and non-GLP Tox services for both small, large molecule and new modality drugs such as proteins, antibodies, peptides, oligonucleotides, cell and gene therapy, mRNA, PROTAC and XDC. We have all common laboratory animal species such as non-human primates, dogs, minipigs, mice, rats, and rabbits available.
Additionally, Medicilon boasts extensive experience in PK studies of ophthalmic drugs and inhaled drug delivery systems, encompassing a range of animal species such as rodents, rabbits, dogs, and monkeys. We offer a variety of delivery methods to accommodate the diverse requirements of drug studies during the preclinical phase.

❖Liver microsomes/S9/Hepatocyte metabolic stability
❖CYP450 enzyme inhibition & TDI
❖CYP450 enzyme induction
❖Enzyme phenotype analysis
❖Plasma protein binding
❖Plasma (serum) stability
❖In vitro MetID and metabolic pathways
❖GSH-trapping
❖Whole blood/plasma distribution
❖Permeability and efflux
❖Transporters(P-gp/BCRP/OATs/OCTs/OATPs/MATEs/BSEP/MRPs)
❖BBB penetration,Kp,uu
❖hERG
❖Mini-Ames, Ames
❖Species:Mouse (ICR, C57, balb/c, SCID, Nude mouse), Rat (SD, Wistar), Guinea pig, Mini-pig, Rabbit, Canine (beagle dog), Cynomolgus monkey
❖Administration Routes: Intravenous (IV), Oral (PO), Subcutaneous (SC), Intramuscular (IM), Intraperitoneal (IP), Topical, Transdermal, IT etc.
❖Dose Strategies: Single, multiple and cassette dosing
❖Serial blood microsampling
❖In vivo metabolite identification and quantitation
❖Tissue distribution
❖Mass balance with excretion
❖Pre-formulation screening
❖PK/PD & human PK modeling
❖Tox, MTD, DRF
❖125I/14C/3H labeled isotope drug metabolism and mass balance studies
❖Surgical techniques: Venous cannulation, biliary cannulation, infusion pump, liver/muscle biopsy and implantation
TOP5300 is an orally active follicle stimulating hormone receptor allosteric agonist that provides a preferred treatment for over 16 million infertile women of reproductive age in low complexity methods or in high complexity methods. TOP5300 represents a new allosteric agonist with potential for ovarian stimulation in women. The safety profile demonstrated lack of toxicity.
TOP5300 was evaluated in standard ADME, including Cytochrome P450 inhibition, clearance and pharmacokinetic profiles. Toxicological evaluations were performed in both rat and dog as the second species according to the guidance from FDA. These assays were performed by Medicilon.

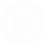
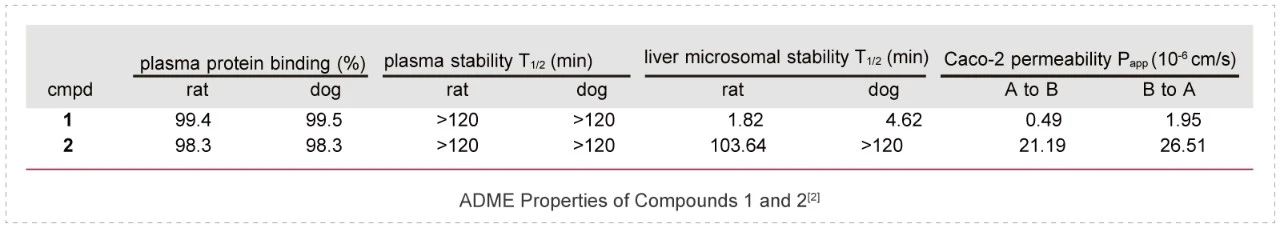
Aberrant activation of the PI3K pathway has been intensively targeted for cancer therapeutics for decades. In this work, researchers designed and synthesized a novel photocaged PI3K inhibitor 1, which could be readily activated by UV irradiation to release a highly potent PI3K inhibitor 2.
To elucidate the difference in ADME properties between compounds 1 and 2, several studies were conducted including plasma protein binding assays, plasma, and liver microsomal stability assays as well as Caco-2 permeability assays. Both compounds showed high plasma protein binding (>98%) as well as a long plasma half-life (>120 min) in rat and dog.
In the liver microsomal stability assay, compound 1 showed a much shorter half-life than the uncaged compound 2. In addition, compound 1 was much less permeable compared to compound 2 in the Caco-2 assay, which may be attributed to its largely increased molecular size. ADME studies of compounds 1 and 2 were conducted by Medicilon.
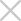
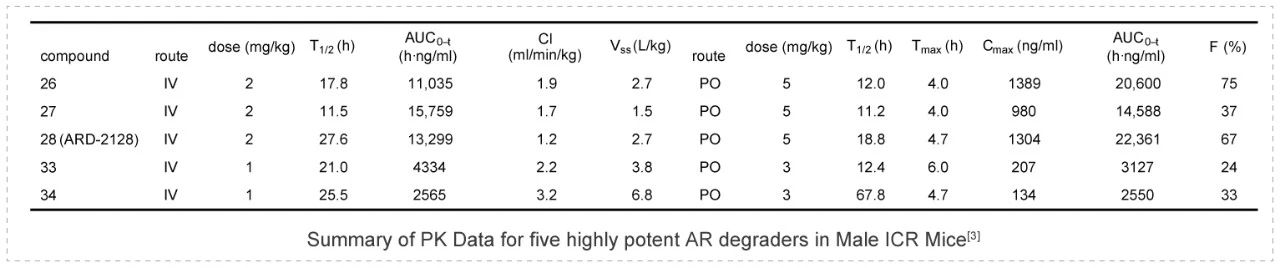
ARD-2128 is a bona fide PROTAC AR degrader and strongly suppresses AR-regulated genes in a dose- and time-dependent manner in AR+ prostate cancer cell lines. The PK data show that ARD-2128 has a low clearance (1.2 mL/min/kg) and a moderate to high steady-state volume of distribution (Vss) of 2.7 L/kg. ARD-2128 exhibits a long half-life following both intravenous (2 mg/kg, i.v.) and oral administration (5 mg/kg, p.o.) with the T1/2s of 27.6 h and 18.8 h, respectively. ARD-2128 (5 mg/kg, p.o.) achieves 67% oral bioavailability in mice, effectively reduces AR protein and suppresses AR-regulated genes in tumor tissues after oral administration, leading to the effective inhibition of tumor growth in mice without signs of toxicity. PK studies were performed in Medicilon.
The plasma and microsomal stability data show that ARD-2128 has excellent plasma and microsomal stability in in mouse, rat, dog, monkey, and humans.The stability was studied in Medicilon.

ARD-2585 is an exceptionally potent and orally active AR degrader. ARD-2585 is a promising androgen receptor (AR) degrader suitable for further extensive evaluations for the treatment of AR+ prostate cancer and other human diseases in which AR plays a key role.
Researchers evaluated ARD-2585 for its liver microsomal stability in five different species (human, mouse, rat, dog, and monkey). ARD-2585 showed excellent stability in liver microsomes in all the five species with T1/2>120 min. The excellent mouse microsomal stability data are consistent with the slow clearance of ARD-2585 seen in the PK data in mice. The liver microsomal stability assay was performed by Medicilon.
Researchers tested ARD-2585 for its plasma stability in five different species (human, mouse, rat, dog, and monkey). ARD-2585 showed excellent plasma stability in all 5 species with T1/2>120 min. The plasma stability assay was performed by Medicilon.
In vitro inhibition of the human ERG (the human ether-à-go-go-related gene) channel has been used as an important assay to assess potential cardiotoxicities of a drug molecule. We evaluated ARD-2585 for its inhibition of the hERG channel and found that ARD-2585 exhibits no hERG inhibition up to 30 μM, the highest concentration tested. The hERG assay was performed by Medicilon.
The ADC molecule raises the difficulties of PK study as each component of the ADC molecule has unique PK characteristics. Medicilon provides high quality quantification assays for key parameters in ADC pharmacokinetic evaluations, presenting accurate results.


Eye Drops Administration to Dutch Rabbits - Small Molecule (Suspension)
Methods: Blood samples were collected at different time points to detect the concentration of test article and calculate the relevant parameters to investigate the PK characteristics in vivo. Eye tissues were collected at 1h and 3h, and the drug concentration at different time was calculated.
Conclusion: For ocular surface administration, systemic exposure is low; The drug concentration in the cornea is relatively high (the drug is distributed more in the anterior segment of the eye and less in the posterior segment of the eye, which is consistent with the PK characteristics of conventional eye drops)

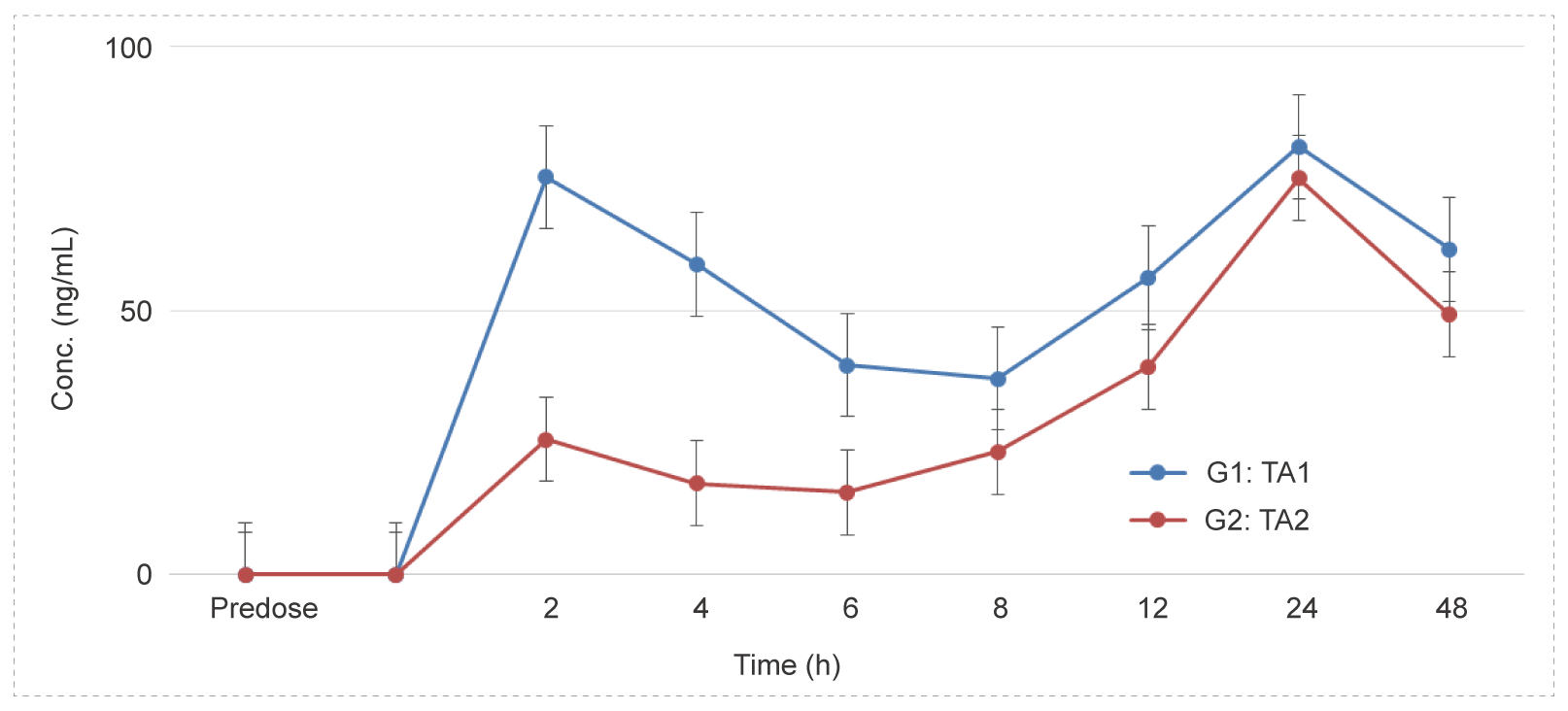
Intravitreal Administration to Dutch Rabbits - Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)
Methods: Blood samples were collected at different time points to detect the concentration of test article and calculate the relevant parameters to investigate the PK characteristics in vivo.
Conclusion: After intravitreal administration, the drug concentration in the serum is not high, the drug lasts for a long time, with a long half-life.
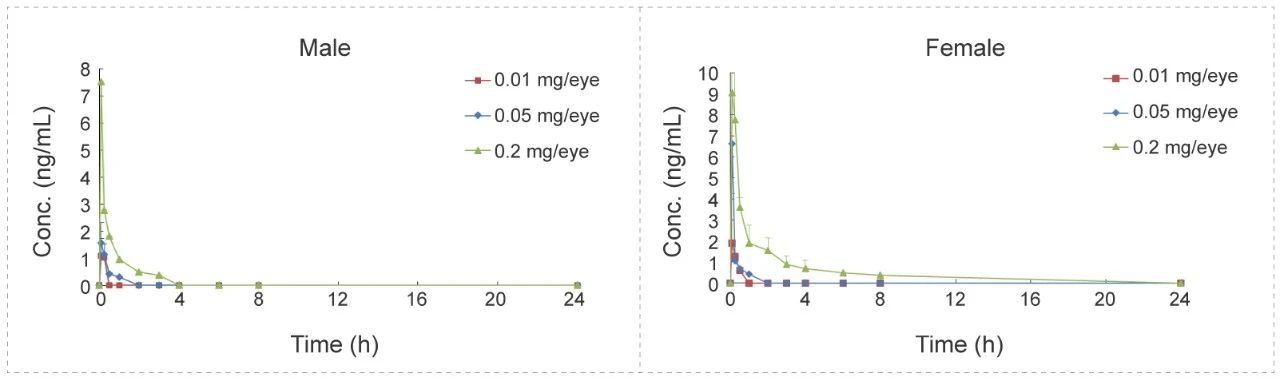
Eye Drops Administration to Beagle Dogs - Small Molecule (Solution)
Methods: Blood samples were collected at different time points to detect the concentration of test article and calculate the relevant parameters to investigate the PK characteristics in vivo.
Conclusion: After eye drops administration, plasma drug exposure is low, with a short half-life. No difference between male and female animals.
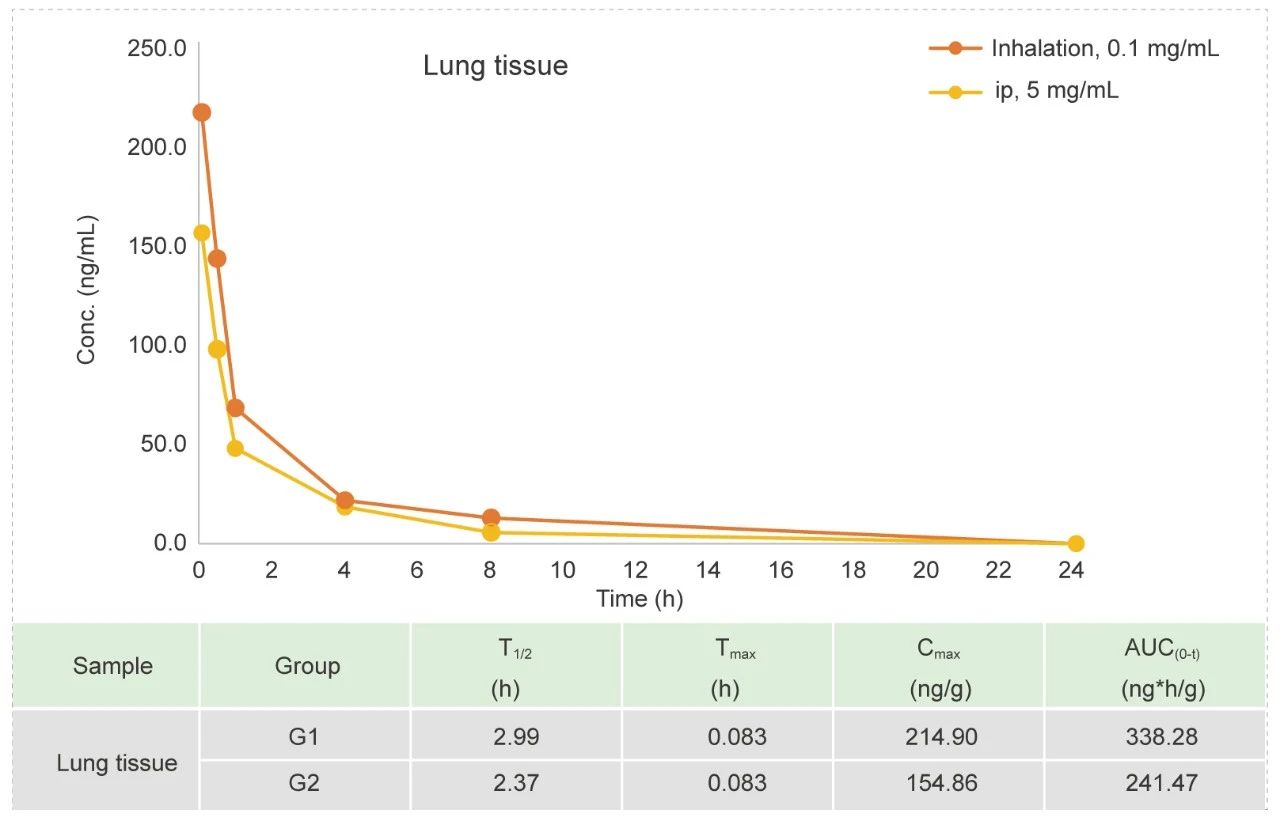
Tracheal atomizer needle in Rat (Liquid)
Methods: Pharmacokinetic studies of ip bolus & inhalation, blood samples were collected at 12 time points.
Conclusion: The exposure amount in lung tissue is higher in inhaled group than ip.
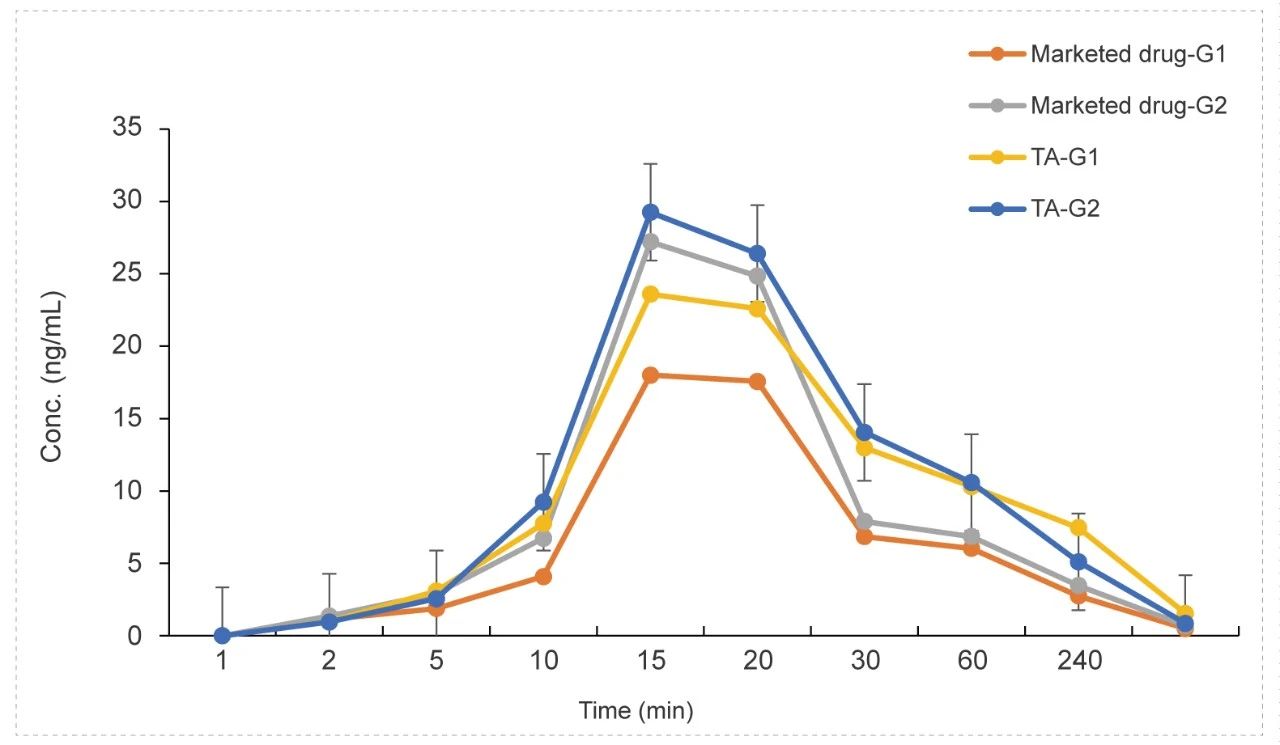
Tracheal atomizer needle in Rat (Dry Powder)
Methods: Pharmacokinetic studies of dry powder administration & tracheal atomizer needle inhalation,blood samples were collected at 9 time points.
Conclusion: The exposure in the low and high dose groups of the test article was higher than the marketed drug control.
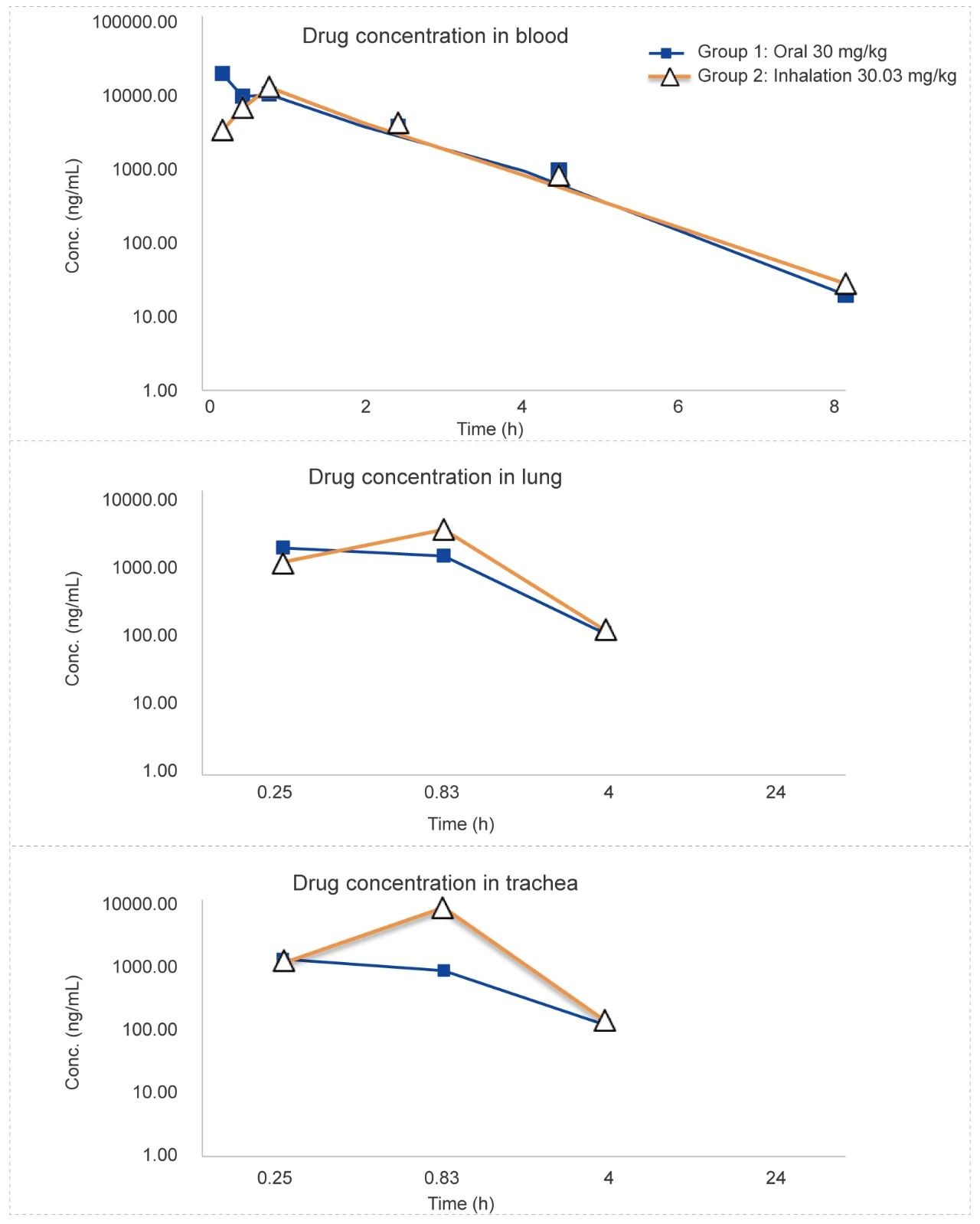
Rat Oronasal Exposure Inhalation Test (for 48 minutes)
Methods: Pharmacokinetic studies of oronasal exposure inhalation & oral administration, the exposure in rat plasma, lung tissue, and trachea (tissue homogenate) was compared after 48 minutes of administration.
Conclusion: The blood concentration of the test article administered by inhalation is higher than administered orally in lung tissue and tracheal tissue homogenates.
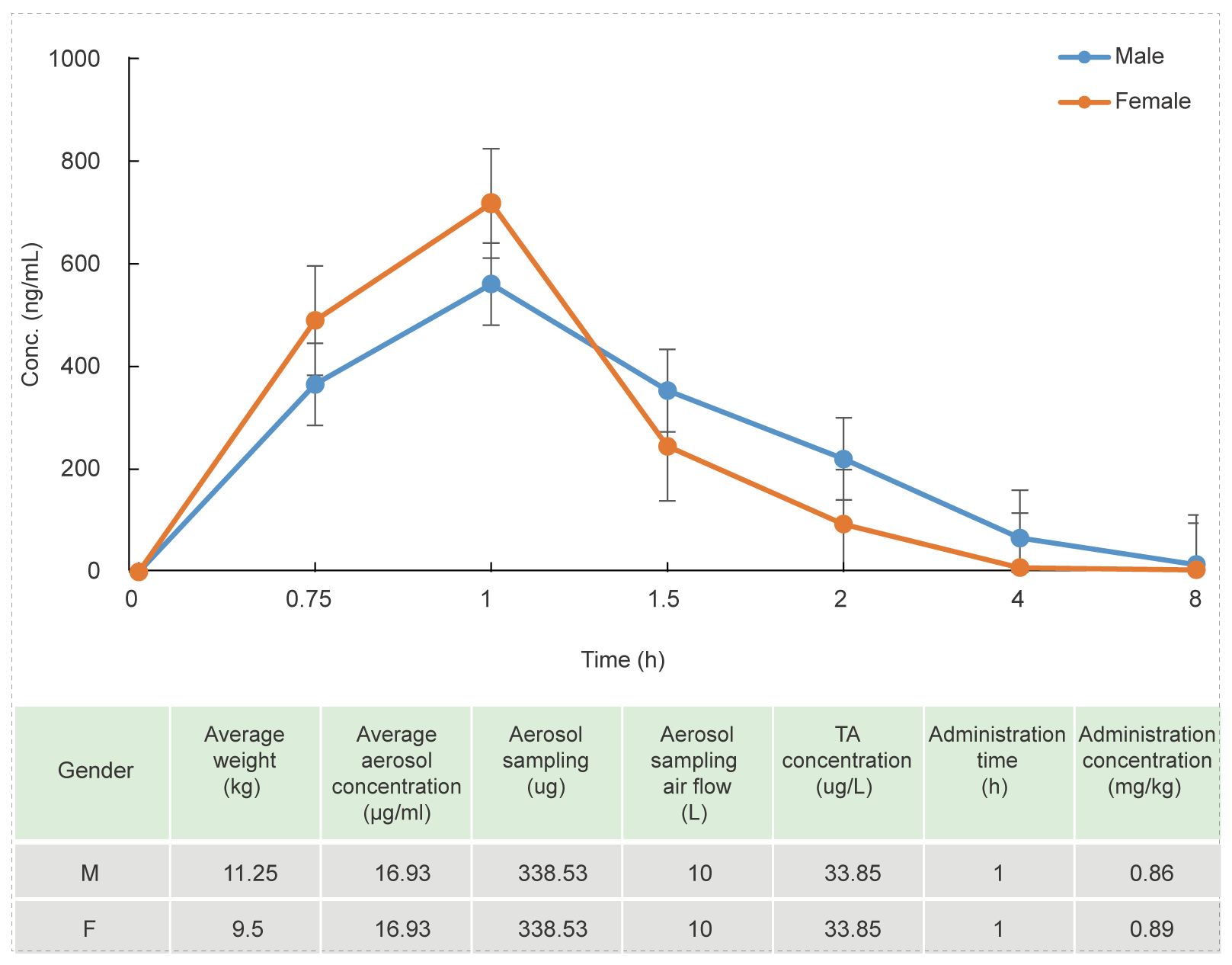
Beagle Dog Oronasal Exposure Inhalation Test (for 1 hour)
Methods: Blood samples were collected at different time points to detect the concentration of test article and calculate the relevant parameters to investigate the PK characteristics in vivo.
Conclusion: The blood concentration reaches the highest level after 1 hour of administration, the aerosol administration concentration of the test article is stable, and the concentration of the test article is stable.
❖Offer a full suite of in vivo ADME and PK services, conducted by a team with 20 years of experience.
❖Maintain an AAALAC-accredited facility with clean rooms for cell culture, an animal care vivarium, and a large variety of instrumentation to perform screening to IND-enabling studies to support compound’s development.
❖Offer our expertise in DMPK & non-GLP/GLP bioanalysis and toxicology, to support you in the complete characterization of the ADME properties and the evaluation of the toxicity of clinical candidate.
❖From our global locations, we serve many of the largest pharmaceutical, specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies in America, Europe and Asia. Our highly trained scientists utilize an extensive range of leading-edge technology, automation and state-of-the-art techniques.
[1] Selva Nataraja, et al. Discovery and Preclinical Development of Orally Active Small Molecules that Exhibit Highly Selective Follicle Stimulating Hormone Receptor Agonism. Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 14;11:602593. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.602593.
[2] Kehui Zhang, et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of a Novel Photocaged PI3K Inhibitor toward Precise Cancer Treatment. J Med Chem. 2021 Jun 10;64(11):7331-7340. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02186.
[3] Xin Han,et al. Strategies toward Discovery of Potent and Orally Bioavailable Proteolysis Targeting Chimera Degraders of Androgen Receptor for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer.J Med Chem. 2021 Sep9;64(17):12831-12854. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00882.
[4] Weiguo Xiang, et al. Discovery of ARD-2585 as an Exceptionally Potent and Orally Active PROTAC Degrader of Androgen Receptor for the Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer.J Med Chem.2021 Sep 23;64(18):13487-13509. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00900.
 相關新聞
相關新聞